See also Anatomical terms of location;WebMD's Sinuses Anatomy Page provides a detailed image and definition of the sinuses including their function and location Also learn about conditions, tests, and treatments affecting the sinusesPosterior (or dorsal) means the opposite of anterior "back of" or "behind/on the back" This is easy to remember because "posterior" is another word for your rear end, which is on your backside An anatomy test question might ask, "Your sternum is ________ to your spine" The answer is that your sternum is anterior to the spine

Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
Back of head anatomy term
Back of head anatomy term-Adenoids Adenoids is the term given to the lymphatic tissue collection These tissues are located towards the rear side of the nasal passages which in turn lie in the nasopharynx The adenoids are also known as the "lymph glands"Medial Toward the midline of the body Lateral Away from the midline of the body Proximal Toward a reference point (extremity) Distal Away from a reference point (extremity) Inferior Lower or below Superior Upper or above Cephalad or Cranial Head Caudal or Caudad Tail, tail end Anterior Toward the front


Anatomical Terminology
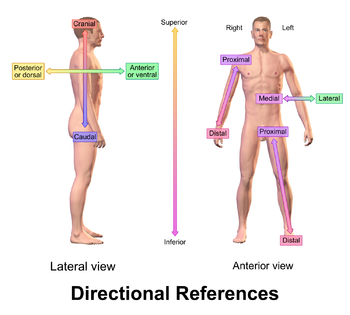
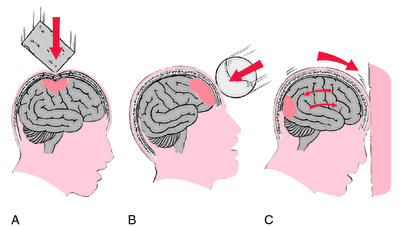
For instance, a full understanding of the subject of local anaesthesia requires knowledge of the skull and oral anatomy, as well as of the drugs used Anatomy of the skull The skull is the topmost part of the bony skeleton of the body, the head, and is made up of three main areas Cranium – the hollow cavity which surrounds the brainCertain directional anatomical terms appear throughout this and any other anatomy textbook (Figure 2) These terms are essential for describing the relative locations of different body structures For instance, an anatomist might describe one band of tissue as "inferior to" another or a physician might describe a tumor as "superficial toRegions of the body are identified using terms such as "occipital" that are more precise than common words and phrases such as "the back of the head" Directional terms such as anterior and posterior are essential for accurately describing the relative locations of body structures
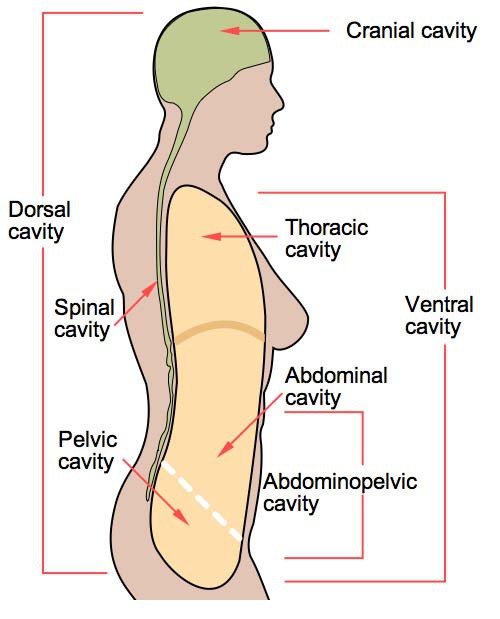
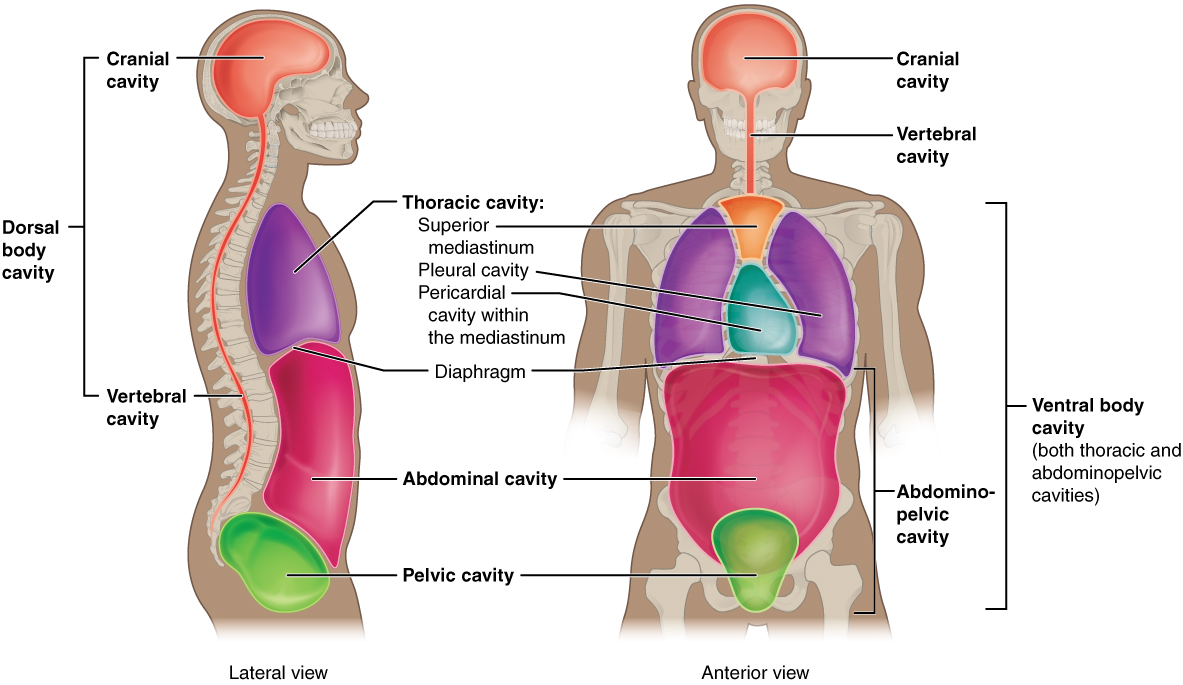
Body cavities – hollow spaces within the human body that contain internal organs a)The dorsal cavitylocated toward the back of the body, is divided into the cranial cavity (which holds the brain) and vertebral or spinal cavity (which holds the spinal cord)The loin Term Manus Definition Pertaining to the hand Term Terms used primarily to locate areas of body limbs TermUsually, headaches in the back of head are the result of stress, muscle tightness, tension, the overuse of medications, and tiredness Sometimes a pain in the base of your skull can be caused by Occipital neuralgia which is a condition that affects the nerves that run from the top of the spinal cord up through the scalp
• The basal ganglia are a cluster of structures in the center of the brain The basal ganglia coordinate messages between multiple other brain areas • The cerebellum is at the base and the back ofThe frontal plane, also referred to as the coronal plane, which is shown in the picture above, is the imaginary line that separates the front from the back of the body The term used for the front of the body is the ventral surface and the term used for the back of the body is the dorsal surface of the bodyOcciput back of head;
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11167/body-planes-and-directional-terms_english.jpg)


Basic Anatomy Terminology Organ Systems Major Vessels Kenhub


Anatomical Terms Meaning Anatomy Regions Planes Areas Directions
The head louse anatomy The anus is situated at the back of the abdomen and close to the genitals The males have a rounded back end, but this may appear pointed because the penis often protrudes through the genitals The back end of the females, on the other hand, is clearly WshapedIn terms of anatomy, the body is divided into regions In the front, the trunk is referred to as the "thorax" and "abdomen" The back as a general area is the dorsum or dorsal area, and the lower back is the lumbus or lumbar regionThe shoulder blades are the scapular area and the breastbone is the sternal region The abdominal area is the region between the chest and the pelvisIn terms of anatomy, the body is divided into regions In the front, the trunk is referred to as the "thorax" and "abdomen" The back as a general area is the dorsum or dorsal area, and the lower back is the lumbus or lumbar regionThe shoulder blades are the scapular area and the breastbone is the sternal region The abdominal area is the region between the chest and the pelvis



Crown Of Head Conditions Injuries And More



Anatomical Directional Terminology Anterior Posterior And More Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
They act like an expansion joint This allows the bone to enlarge evenly as the brain grows and the skull expands The result is a symmetrically shaped head Some sutures extend to the forehead, while others extend to the sides and back of the skull One suture in the middle of the skull extends from the front of the head to the backDorsum back ;Basic Anatomy Terms This medical billing terminology list will help you navigate the CPT and ICD manuals, decipher doctor's reports, and give you a more thorough understanding of the medical practice in general Let's look now at a few basic terms for the regions of the body You might recognize some of them


Anatomical Terms Of Location Wikipedia


Anatomy Of The Head And The References Used For The Areas Of The Head In Haircuts And Haircutting
A feature that is posterior to another is closer to the back of the body when the body is in anatomical position Ventral/Dorsal–Equivalent to bellyside and backside of a body in anatomical position For a human in anatomical position, this pair of terms is equivalent to anterior and posteriorMedial Toward the midline of the body Lateral Away from the midline of the body Proximal Toward a reference point (extremity) Distal Away from a reference point (extremity) Inferior Lower or below Superior Upper or above Cephalad or Cranial Head Caudal or Caudad Tail, tail end Anterior Toward the frontInferior or caudal away from the head;


How Poor Posture Causes Neck Pain



Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
Skin The head and neck is covered in skin and its appendages, termed the integumentary systemThese include hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and sensory nervesThe skin is made up of three microscopic layers epidermis, dermis, and hypodermisThe epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is divided into the following five sublayers or strata, listed in order from outerSee also Anatomical terms of location;References Notes Last edited on 13 November , at 11



Definition Of Hip Pain



Olecranal Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram
Basic Anatomy Terms This medical billing terminology list will help you navigate the CPT and ICD manuals, decipher doctor's reports, and give you a more thorough understanding of the medical practice in general Let's look now at a few basic terms for the regions of the body You might recognize some of themOcciput back of head;For instance, a full understanding of the subject of local anaesthesia requires knowledge of the skull and oral anatomy, as well as of the drugs used Anatomy of the skull The skull is the topmost part of the bony skeleton of the body, the head, and is made up of three main areas Cranium – the hollow cavity which surrounds the brain



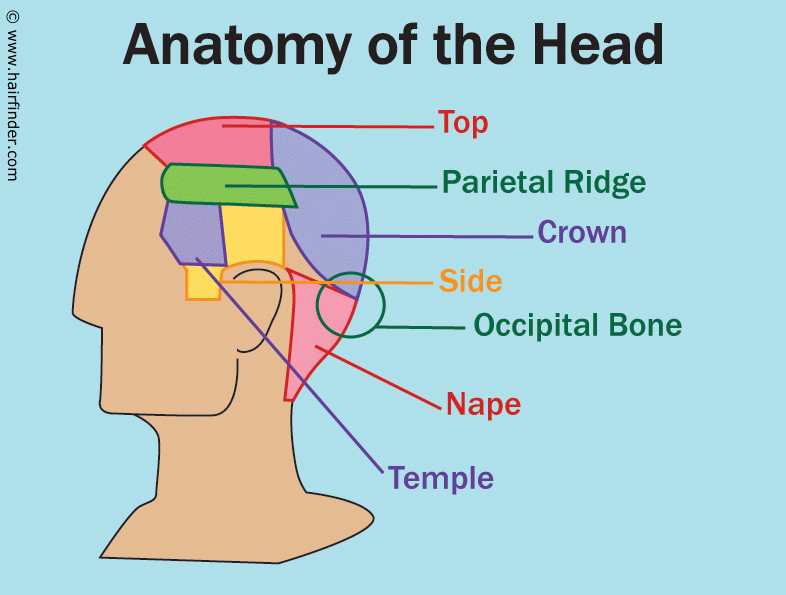
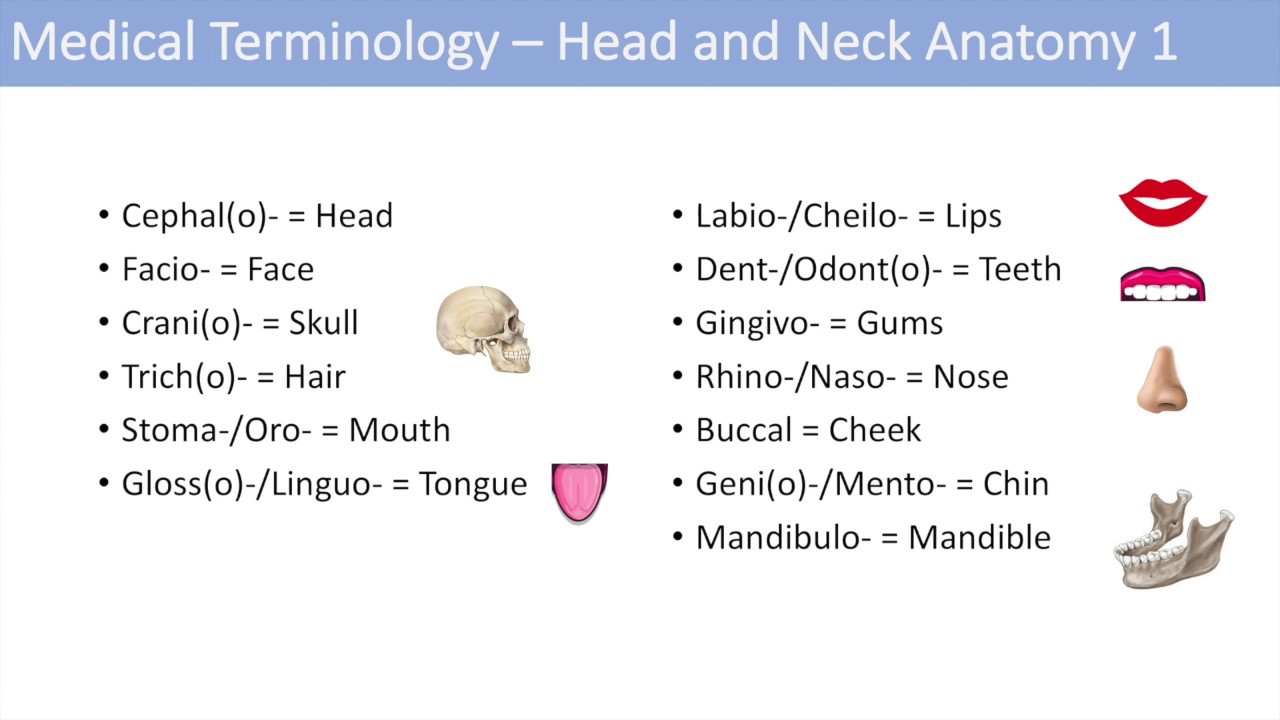
Occipital Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary



Standard Anatomical Position An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cerebellum The cerebellum (back of brain) is located at the back of the head Its function is to coordinate voluntary muscle movements and to maintain posture, balance, and equilibrium More specifically, other parts of the brain include the followingCephalad (or rostral) and Caudal Cephalad means towards the head and caudal means towards the tail bone Dorsal and ventral – dorsal refers to the back and ventral to the front In the human body, these terms are interchangeable with posterior and anteriorA feature that is posterior to another is closer to the back of the body when the body is in anatomical position Ventral/Dorsal–Equivalent to bellyside and backside of a body in anatomical position For a human in anatomical position, this pair of terms is equivalent to anterior and posterior
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11180/regions-of-the-lower-limb_english.jpg)


Anatomical Terminology Planes Directions Regions Kenhub



Week 1 Terms Body Tissues Medical Imaging Studocu
The frontal plane, also referred to as the coronal plane, which is shown in the picture above, is the imaginary line that separates the front from the back of the body The term used for the front of the body is the ventral surface and the term used for the back of the body is the dorsal surface of the bodyChiari malformation is caused by a problem in the back of the skull The skull should have an indented space in the back of the head The rear lower part of the brain and the brainstem are in this space In some people, this indented skull space does not develop well1 human anatomy denoting the back surface of the body Often used to indicate the position of one structure relative to another, that is, nearer the back of the body Synonym (s) dorsalis TA, dorsal (2), posticus 2
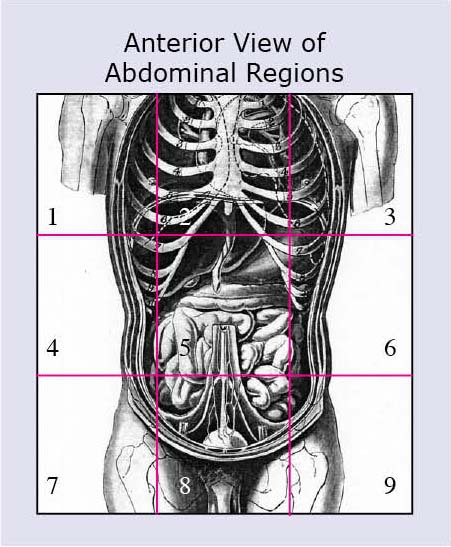


Anatomical Terms Meaning Anatomy Regions Planes Areas Directions



Anatomical Terminology Worksheet Tchs
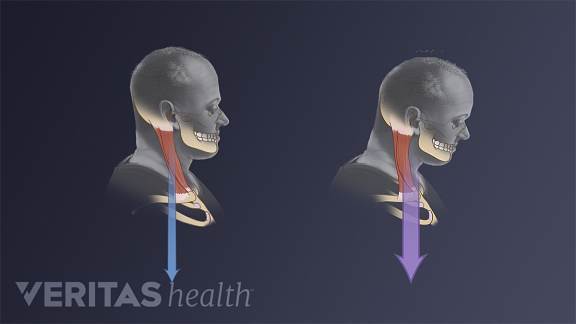
Herniated disks in the cervical spine (neck) can cause neck pain and tension This can cause a type of headache called a cervicogenic headache The pain typically originates and is felt in the backHead hed 1 the anterior or superior part of a structure or organism 2 in vertebrates, the part of the body containing the brain and the organs of special sense Called also caput articular head an eminence on a bone by which it articulates with another bone head injury traumatic injury to the head resulting from a fall or violent blow Such anForward head posture is often accompanied by forward shoulders and a rounded upper back, which can lead to more pain in the neck, upper back, and/or shoulders The longer that poor posture is continued—such as being hunched over a computer or slouching on the couch—the more likely that neck pain, stiffness, and other symptoms may develop
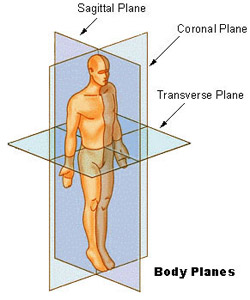


Seer Training Anatomical Terminology


Basic Human Anatomy Distance Learning Course
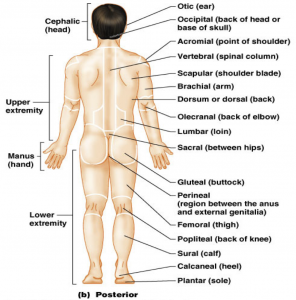
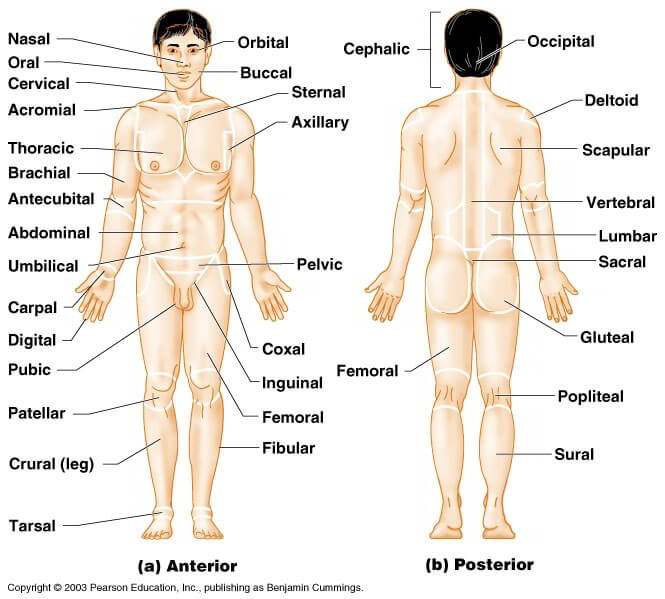
The human back, also called the dorsum, is the large posterior area of the human body, rising from the top of the buttocks to the back of the neck It is the surface of the body opposite from the chest and the abdomenThe vertebral column runs the length of the back and creates a central area of recession The breadth of the back is created by the shoulders at the top and the pelvis at the bottomReferences Notes Last edited on 13 November , at 11The human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart, head and toes pointed forward, and arms hanging at the sides with palms facing foward Pertaining to the area of the back between the ribs and hips;



Anatomical Planes Of The Body
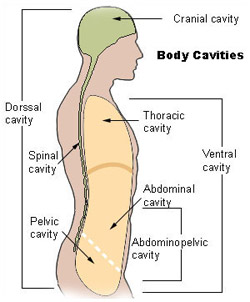


Seer Training Anatomical Terminology
Anterior refers to the 'front', and posterior refers to the 'back' Putting this in context, the heart is posterior to the sternum because it lies behind it Equally, the sternum is anterior to the heart because it lies in front of itHead and Neck Terms and Definitions Head and Neck Equivalent Terms, Definitions, Charts, Tables and Illustrations C000C148, C300C329 (Excludes lymphoma and leukemia – M9590 – 99 and Kaposi sarcoma M9140) Table 1 –Paired Sites Table Instructions Use this table to determine multiple primary status for sites listed in Column 1 Column 1Directional anatomical terms are essential for describing the relative locations of different body structures For instance, an anatomist might describe one band of tissue as "inferior to" another or a physician might describe a tumor as "superficial to" a deeper body structure These terms usually come in pairs, with one word meaning a specific direction and the paired word meaning
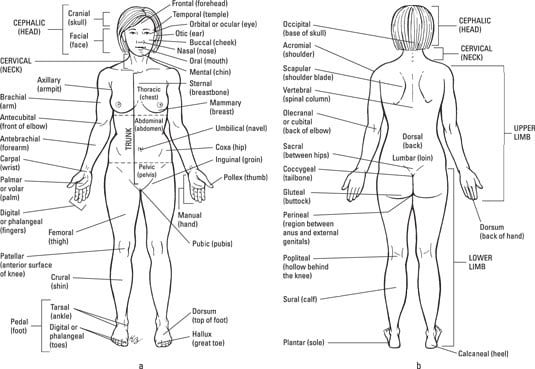


The Anatomical Regions Of The Body Dummies


Anatomical Terminology
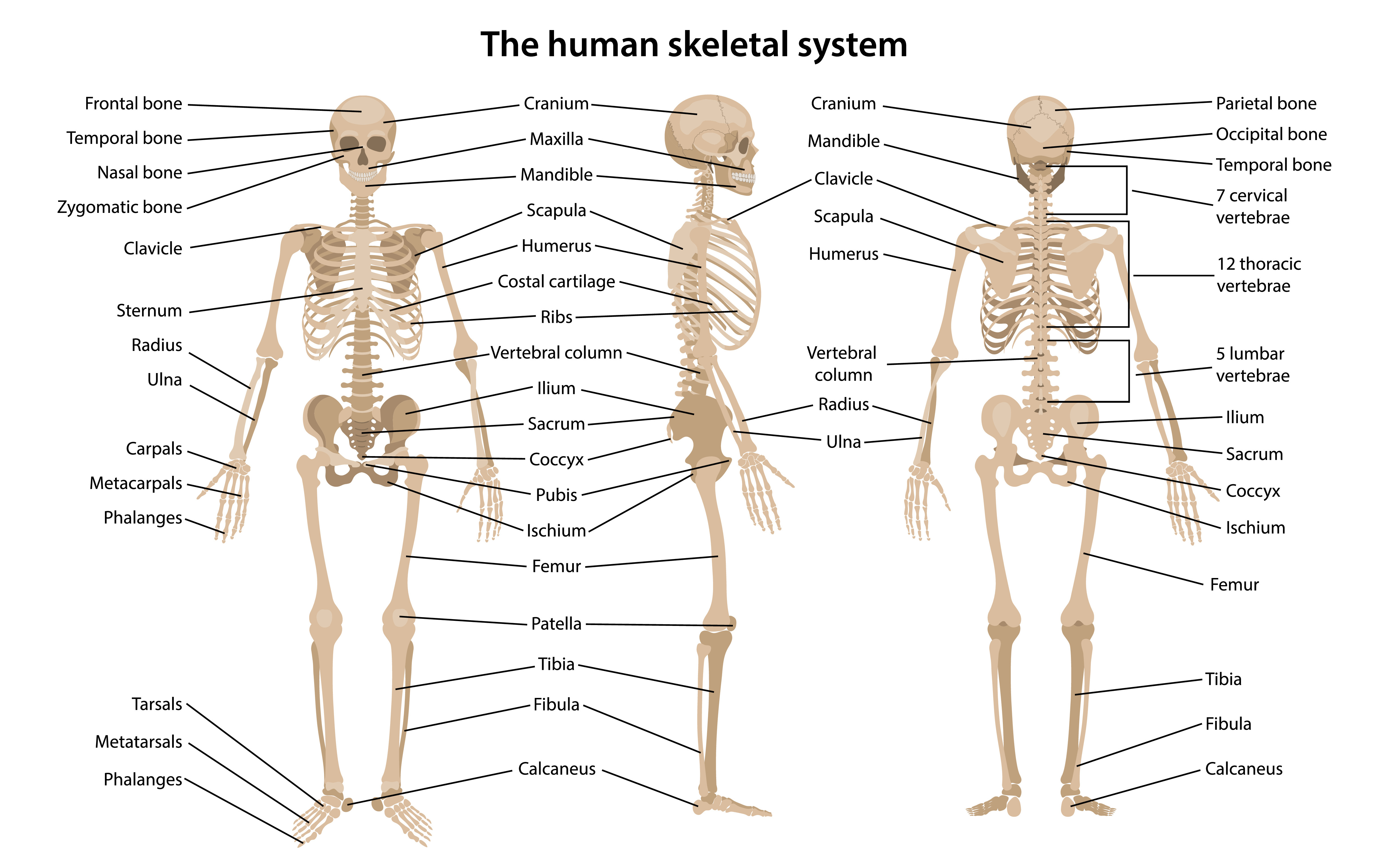
Introduction to the Occipital bone anatomy The occipital bone ( L, occipital – "back of the head" ) is a cranial bone that surrounds the back and base regions of the brain Along with its inferior and internal surfaces is the prominent foramen magnum, which allows the spinal cord to pass through the skullCertain directional anatomical terms appear throughout this and any other anatomy textbook (Figure 2) These terms are essential for describing the relative locations of different body structures For instance, an anatomist might describe one band of tissue as "inferior to" another or a physician might describe a tumor as "superficial toAnatomical Directional Terms Anterior In front of, front Posterior After, behind, following, toward the rear Distal Away from, farther from the origin Proximal Near, closer to the origin Dorsal Near the upper surface, toward the back Ventral Toward the bottom, toward the belly Superior Above, over Inferior Below, under Lateral Toward the side, away from the midline Medial Toward



Standard Anatomical Terms And Planes Medictests


Anatomical Terminology Anatomy And Physiology I
They act like an expansion joint This allows the bone to enlarge evenly as the brain grows and the skull expands The result is a symmetrically shaped head Some sutures extend to the forehead, while others extend to the sides and back of the skull One suture in the middle of the skull extends from the front of the head to the backReferences Notes Last edited on 13 November , at 11Dorsum back ;



Muscles Of The Head And Neck Anatomy Pictures And Information



Neck Anatomy Britannica
Directional anatomical terms are essential for describing the relative locations of different body structures For instance, an anatomist might describe one band of tissue as "inferior to" another or a physician might describe a tumor as "superficial to" a deeper body structure These terms usually come in pairs, with one word meaning a specific direction and the paired word meaningDorsum back ;The dorsal (from Latin dorsum 'back') surface of an organism refers to the back, or upper side, of an organism If talking about the skull, the dorsal side is the top The ventral (from Latin venter 'belly') surface refers to the front, or lower side, of an organism



Head Back And Neck Injuries Altus Emergency Centers 24 7


The Human Body And Anatomy Vocabulary Learn English Vocabulary
Anterior refers to the 'front', and posterior refers to the 'back' Putting this in context, the heart is posterior to the sternum because it lies behind it Equally, the sternum is anterior to the heart because it lies in front of itAlternative Title cephalon Head, in human anatomy, the upper portion of the body, consisting of the skull with its coverings and contents, including the lower jawLower (example, the foot is part of the inferior extremity) Anterior or ventral front (example, the kneecap is located on the anterior side of the leg) Posterior or dorsal back (example, the shoulder blades are located on the posterior side of the body)


Anatomy And Physiology Anatomical Position And Directional Terms



Anatomical Planes Of Body What Are They Types Position In Body
The human back, also called the dorsum, is the large posterior area of the human body, rising from the top of the buttocks to the back of the neck It is the surface of the body opposite from the chest and the abdomenThe vertebral column runs the length of the back and creates a central area of recession The breadth of the back is created by the shoulders at the top and the pelvis at the bottomHuman head (anterior view) The human head is more than just a nuisance responsible for your headaches It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neckIn addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures Muscles of masticationAlternative Title cephalon Head, in human anatomy, the upper portion of the body, consisting of the skull with its coverings and contents, including the lower jaw



1 4 Anatomical Terminology Anatomy Physiology



Solved Xercise 2 Anatomical Terminology Or Language Of A Chegg Com
Occiput back of head;See also Anatomical terms of location;Start studying anatomy common and scientific name (head, neck, and back) Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools


Holes Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy Terms Must Read



Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
Face, front part of the head that, in vertebrates, houses the sense organs of vision and smell as well as the mouth and jaws In humans it extends from the forehead to the chin During the course of evolution from the prehuman Australopithecus to modern humans (Homo sapiens), the face became smaller in relation to the overall size of the headWhile brain and braincase tripled in volume, the



Physiological Psychology
/GettyImages-147219941-56a05efe3df78cafdaa14c5f.jpg)


Superficial Anatomy Of The Back And Core



Anatomical Location Anatomy And Physiology I
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11169/body-surface-anatomy-of-male_english.jpg)


Basic Anatomy Terminology Organ Systems Major Vessels Kenhub
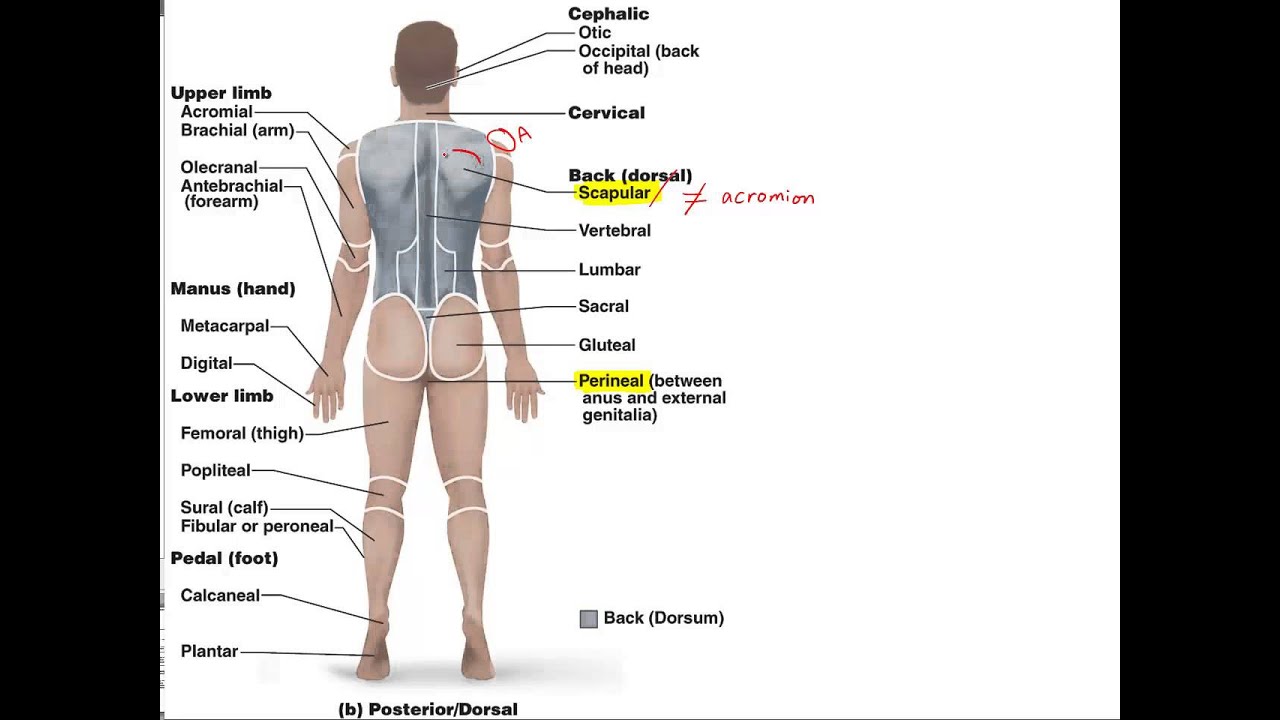


Chapter 1e Anatomical Terminology Youtube


Anatomical Terms Wikiradiography



Anatomical Planes Of The Body



Anatomical Position And Directional Terms Anatomy And Physiology


Anatomical Terms Wikiradiography



Ch01 General Terms General Anatomical Terms
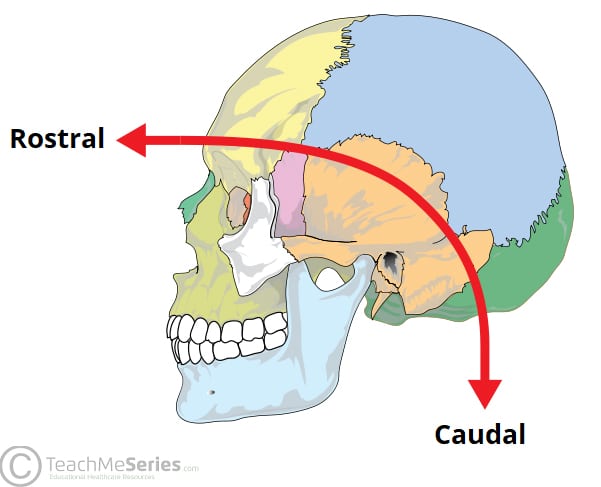


Embryological Terminology Dorsal Ventral Caudal Teachmeanatomy
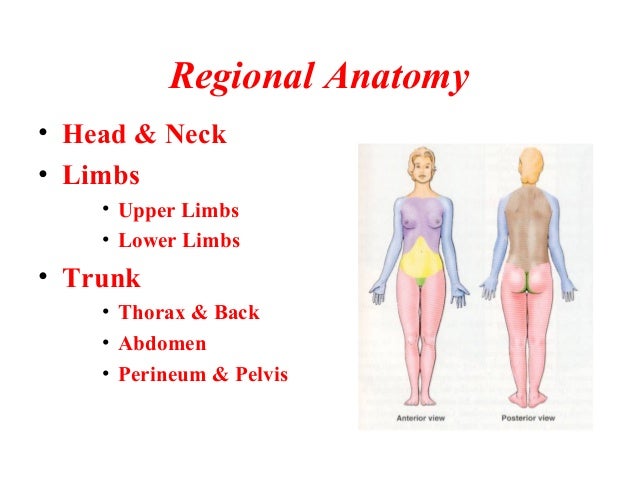


Anatomical Terminology



Pin By Jane Norman On Speech Pathology Tons Of Info Anatomy And Physiology Human Body Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
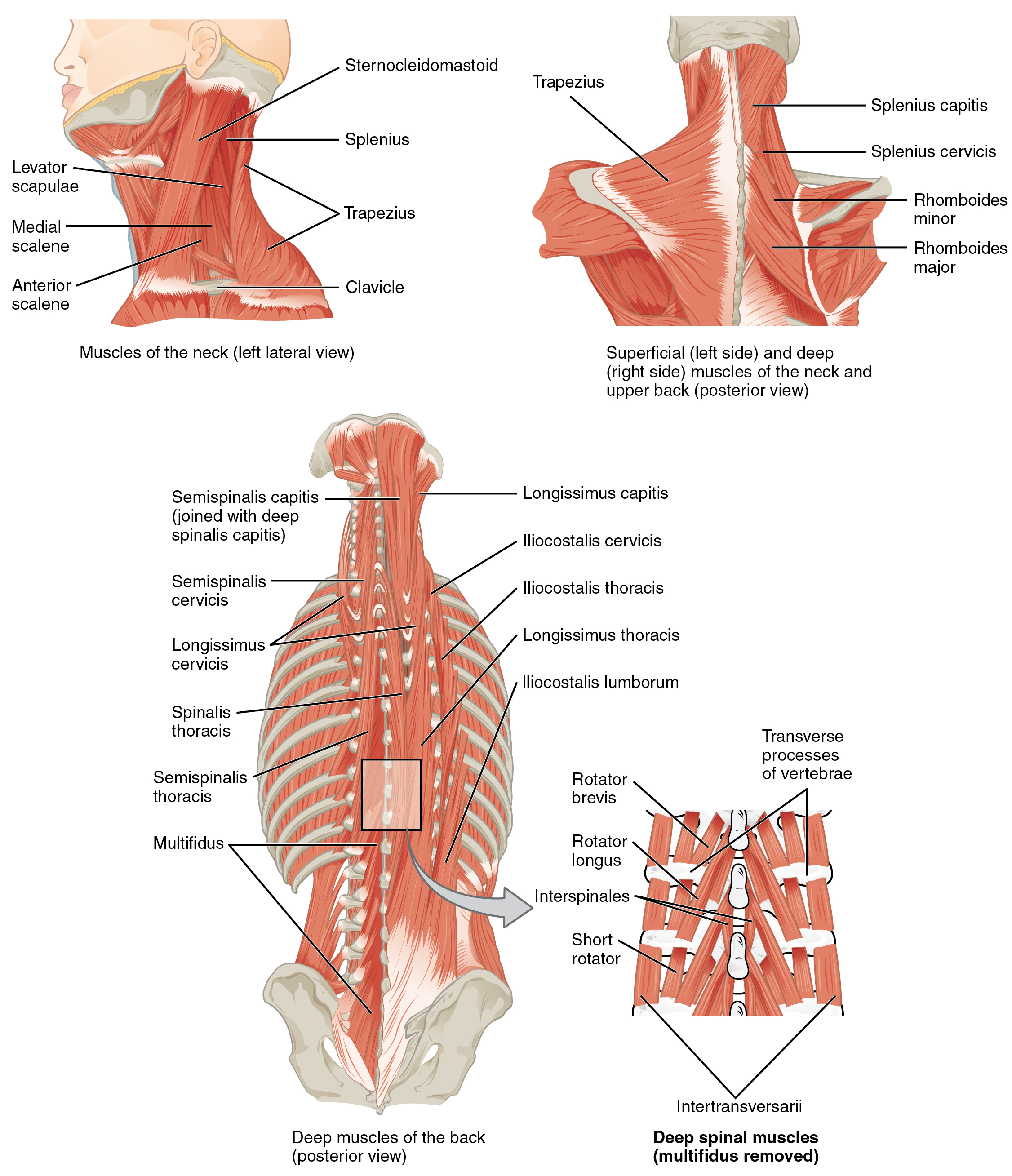


Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology
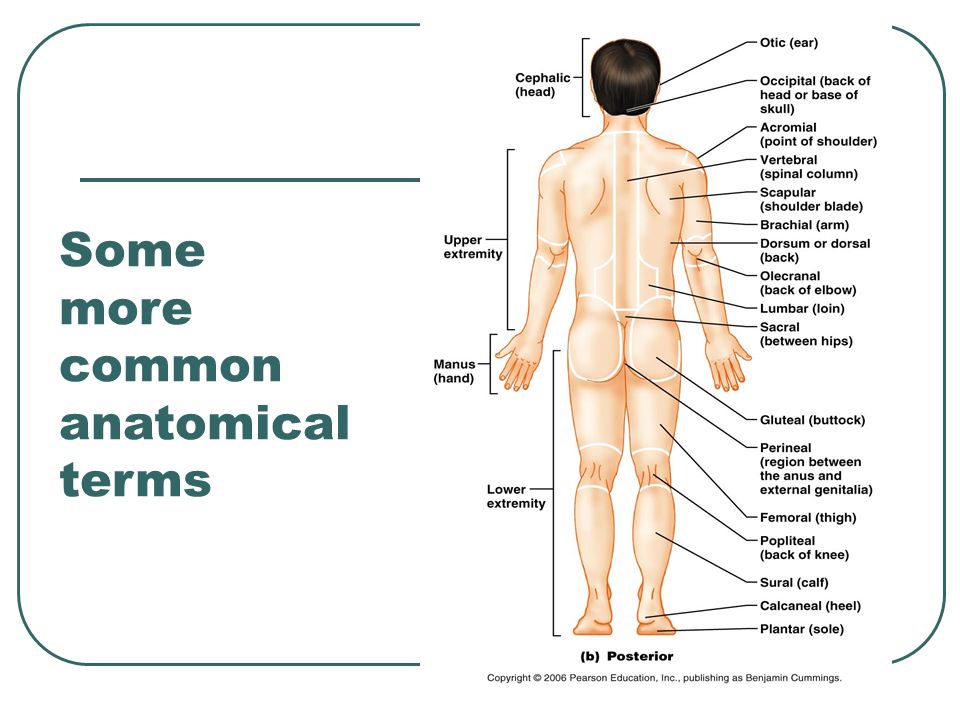


Anatomical Language And Terminology Ppt Video Online Download



Directional Terms Body Regions Medical Terminology Medical Knowledge Medical



Anatomical Position And Directional Terms Anatomy And Physiology



Neck Anatomy Britannica



Directional Terms Quiz Anatomy And Physiology
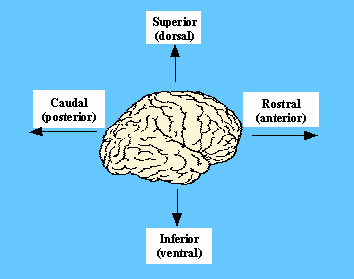


Neuroscience For Kids Directions Planes



Anatomical Plane Wikipedia



Standard Anatomical Position An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
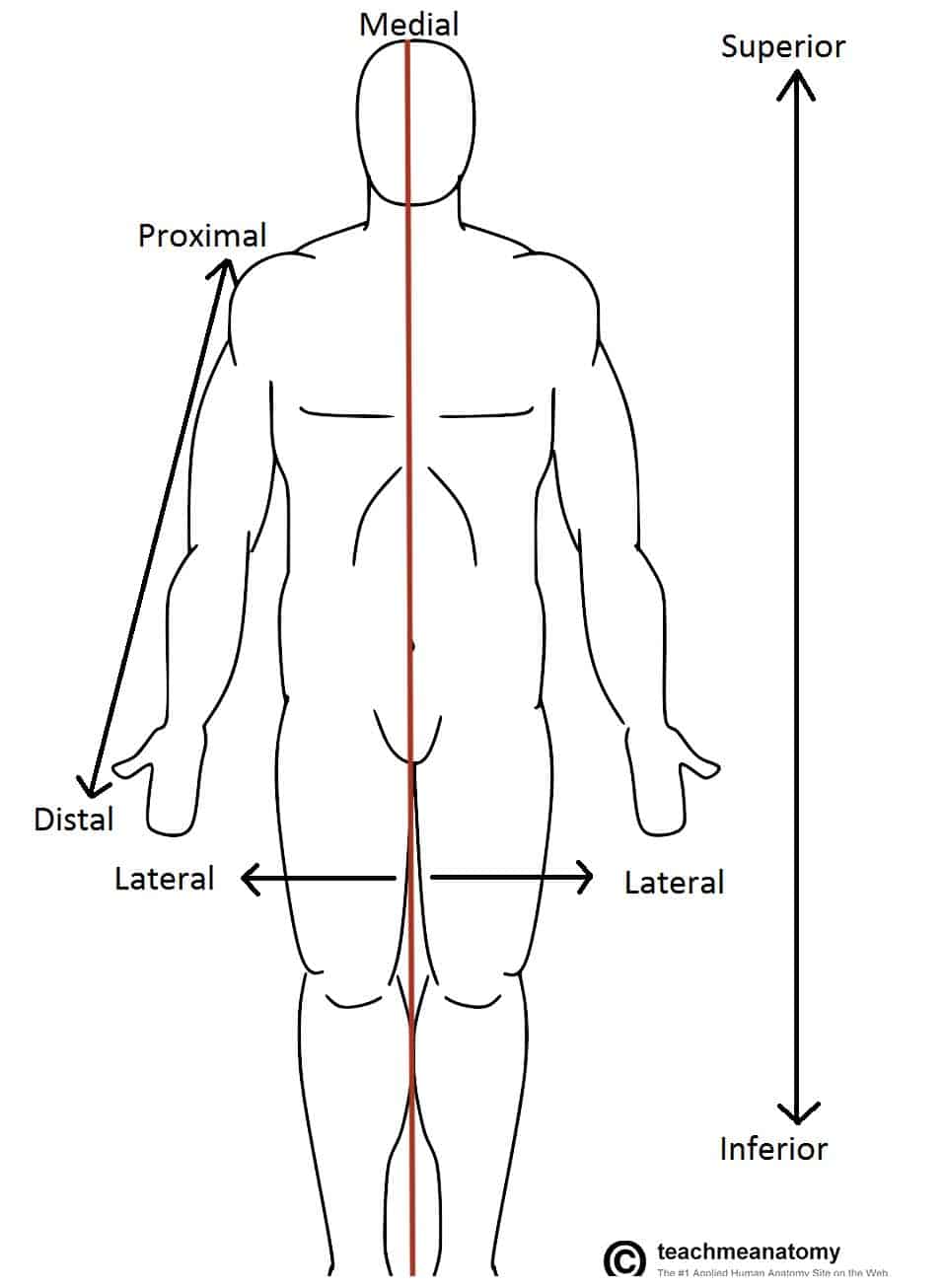


Anatomical Terms Of Location Anterior Posterior Teachmeanatomy



Anatomical Position Definition Of Anatomical Position By Medical Dictionary
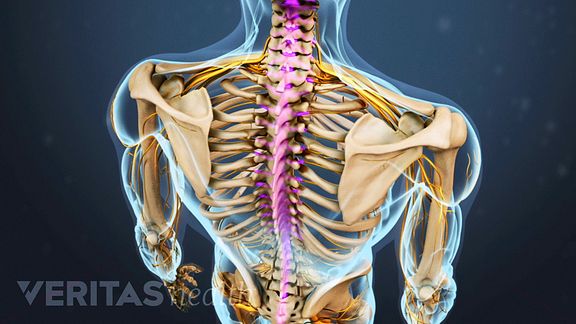


The Basics Of Back Pain And Spinal Anatomy



Nerves Of The Head And Neck Interactive Anatomy Guide


Medical Terminology Lesson 6 Anatomy And Anatomical Terms Youtube


The Temporal Bone Parts Fractures Teachmeanatomy



Anatomical Terminology Diagram Quizlet


Head Anatomy Definition Of Head Anatomy By Medical Dictionary



Anatomy L4 Introduction To Gross Anatomy Skull Flashcards Quizlet



Language Of Anatomy Medical Terminology Study Human Anatomy And Physiology Human Body Anatomy


Directional Terms For Anatomical Position And Major Body Regions Earth S Lab
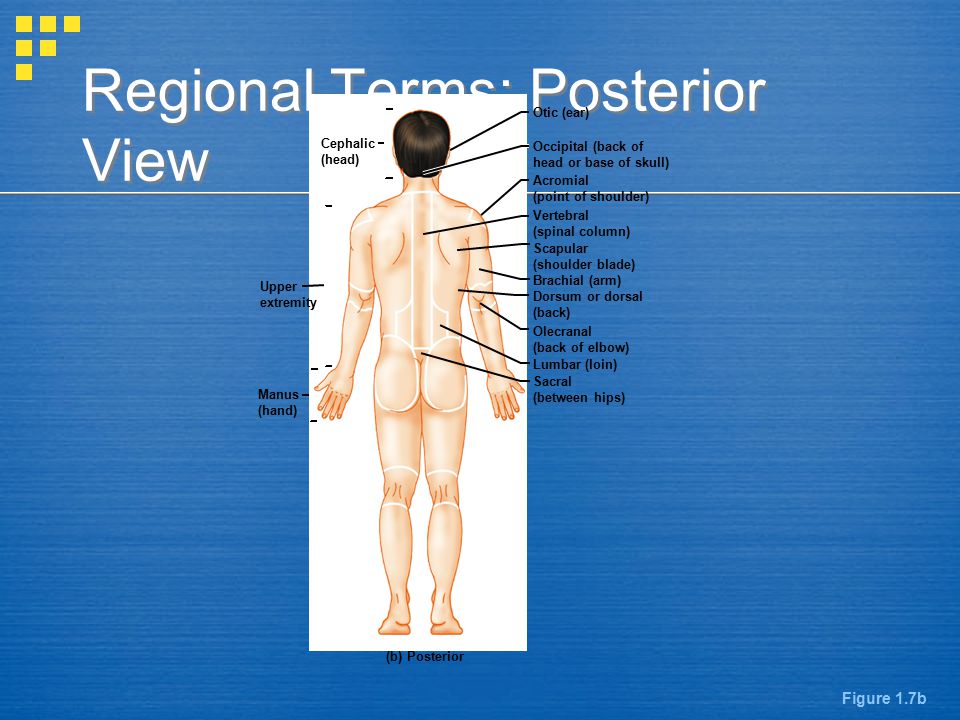


Anatomical Position Body Erect Feet Slightly Apart Palms Facing Forward Thumbs Point Away From Body Figure 1 7a Ppt Video Online Download
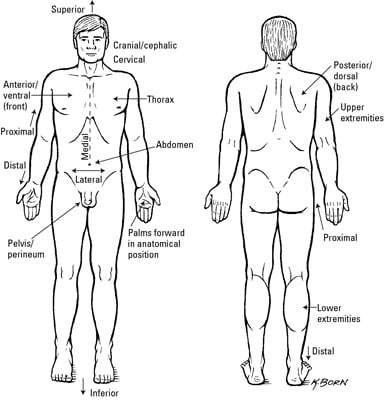


Clinical Anatomy Terms To Describe The Eight Body Regions Dummies
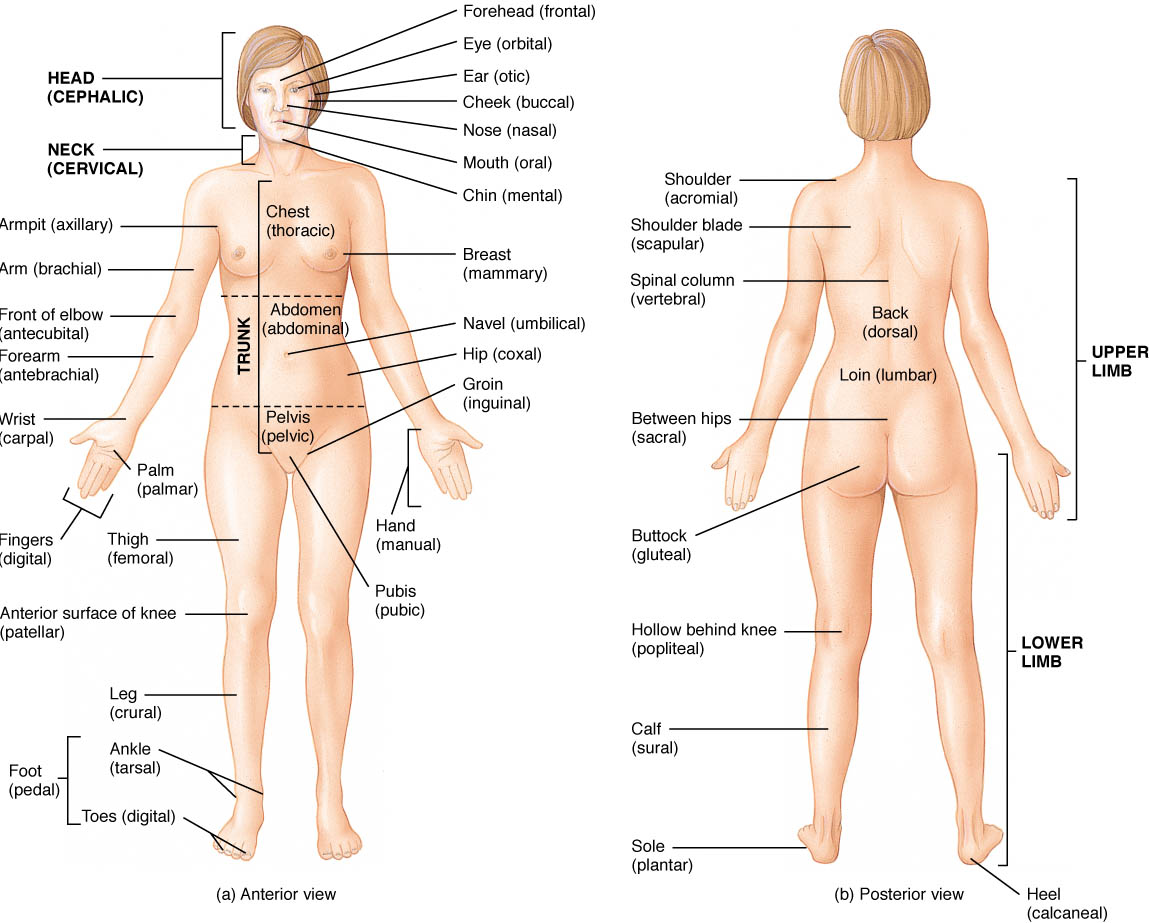


The Language Of Anatomy Anatomical Position And Directional Terms Anatomy Physiology
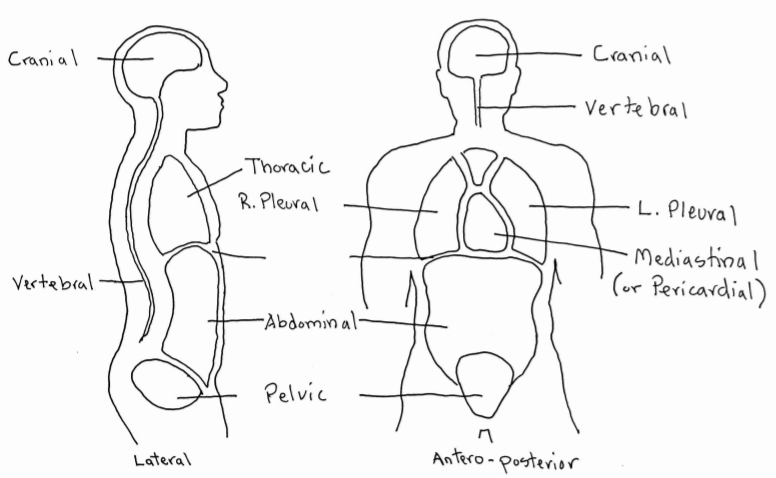


Chapter 03 Anatomical Direction Wtcs Medical Terminology



Standard Anatomical Position An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


A Quick Start On Anatomical Directions John Hawks Weblog
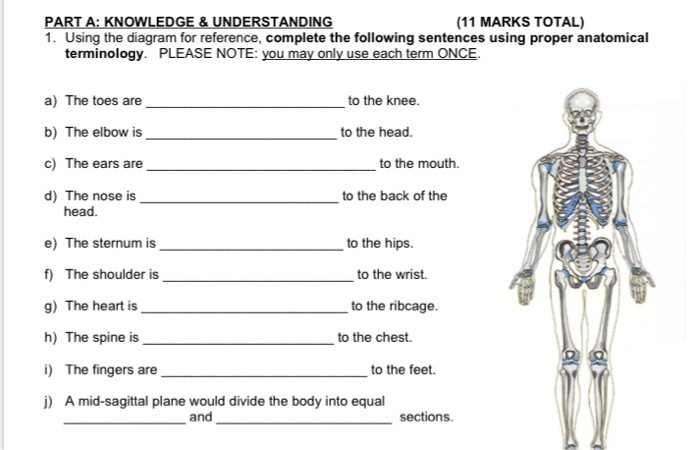


Solved Part A Knowledge Understanding 11 Marks Total Chegg Com
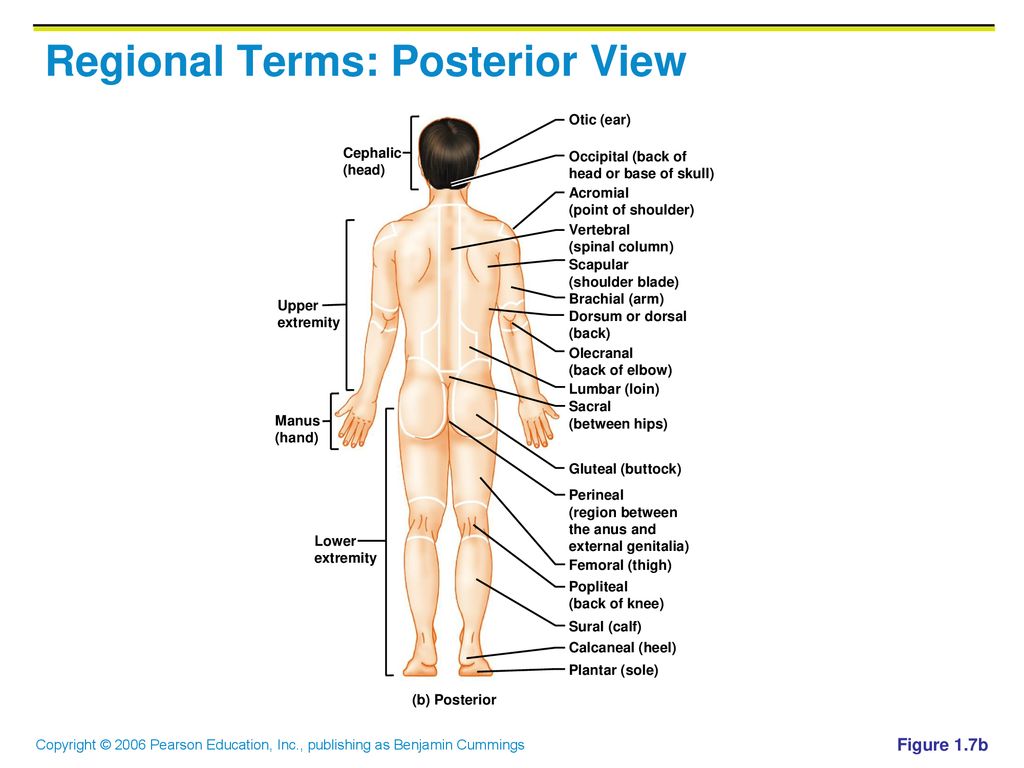


Anatomical Position Universally Accepted Standard Position Ppt Download



Anatomical Terms
/anatomical-directional-terms-and-body-planes-373204-01-28f62bf8f2214f71b9d38dfa85beccb5.png)


Anatomical Directional Terms And Body Planes



Cranial Cavity Wikipedia
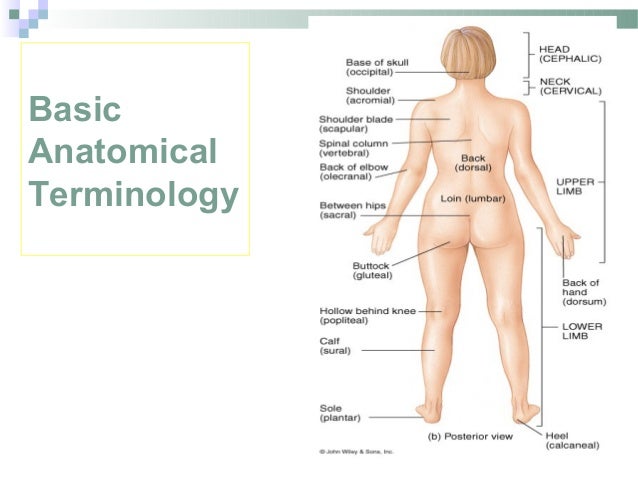


Introduction To Anatomy



Cervical Dysfunction And Pain In The Head And Neck Causes And Osteopathic Options


The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy And Physiology Main Lesson



Back Of Head Skull Anatomy Page 1 Line 17qq Com
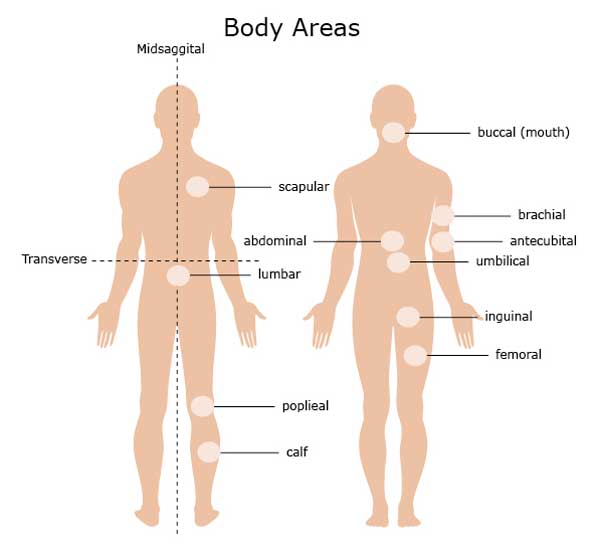


Anatomical Terms Meaning Anatomy Regions Planes Areas Directions
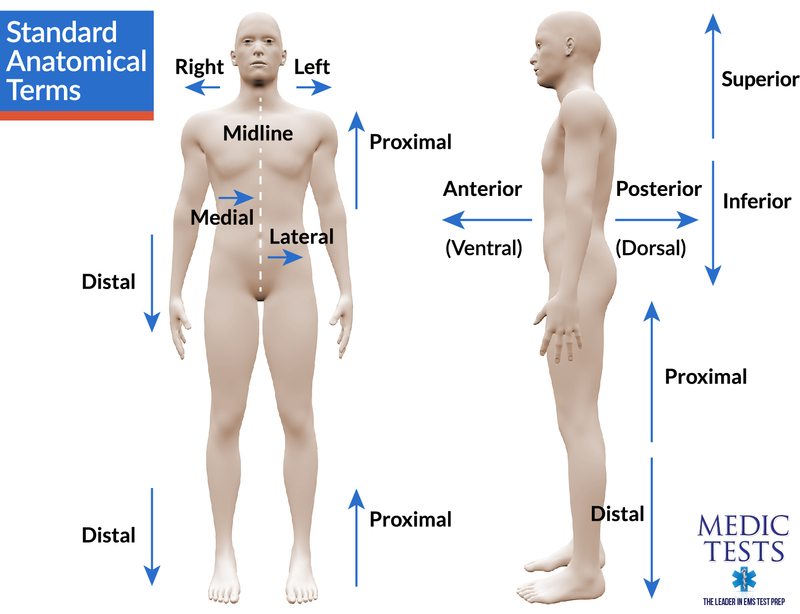


Standard Anatomical Terms And Planes Medictests



Medical Terminology For Health Professions 8e



Physiological Psychology



Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Human Anatomy Openstax Cnx



Anatomical Position And Directional Terms Anatomical Terms Directional Terms Anatomy Youtube



Head Definition Anatomy Britannica


Anatomy And Physiology Anatomical Position And Directional Terms



Humerus Definition Anatomy Fracture Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Anatomical Terminology Anatomy And Physiology I



Anatomical Terminology Crossword Wordmint



Anatomical Terminology The Precise Language Of Anatomy And Physiology 1 5 Body Regions Diagram Quizlet
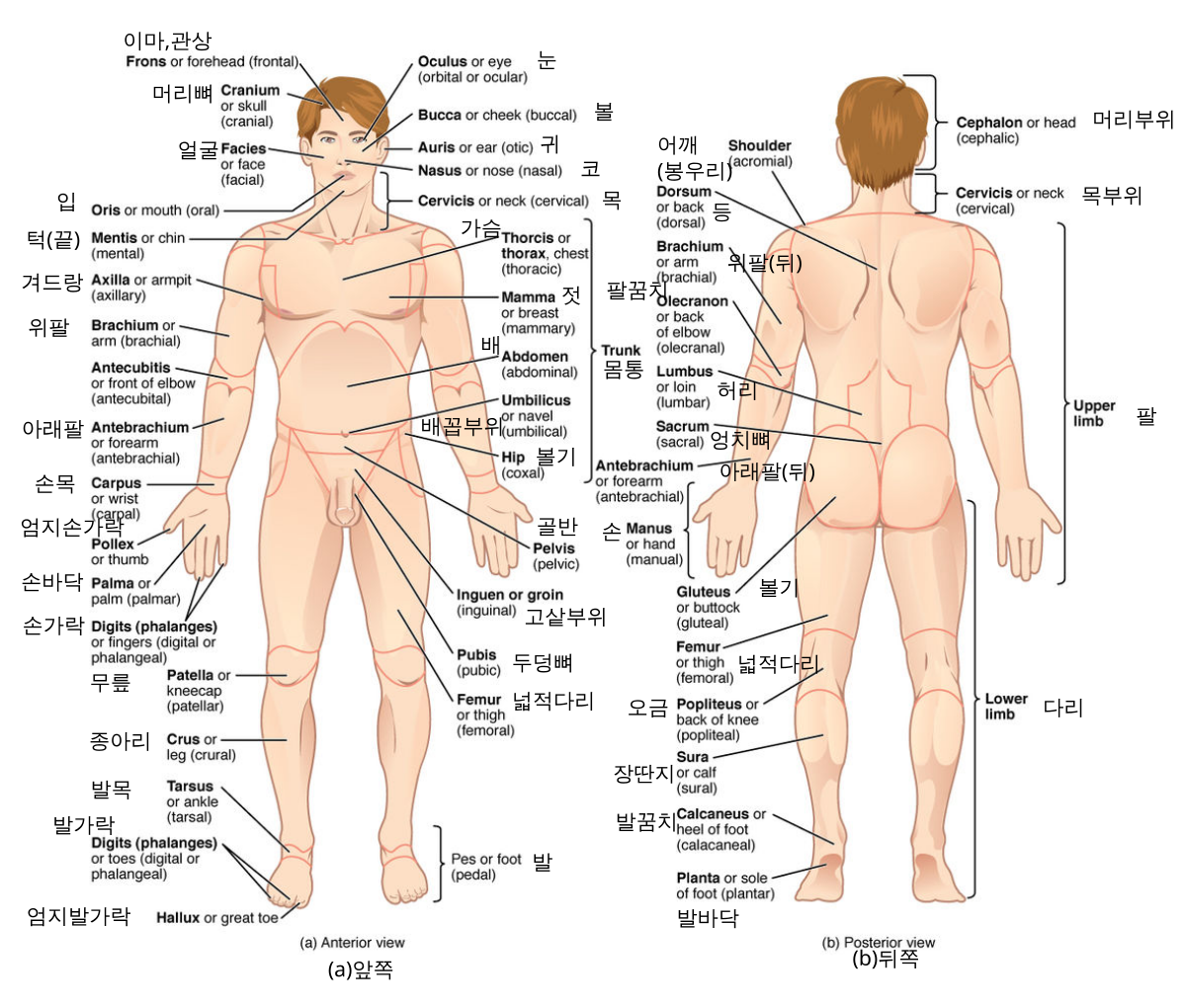


File Anatomical Terminology Enko Svg Wikimedia Commons



Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley



Medical Anatomical Terminology Crossword Wordmint



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿